A unique tax provision, IRC Section 1202 “Qualified Small Business Stock (QSBS)”, was created to incentivize risky capital investments in the innovative startup and early-stage business marketplace in the United States. In the same manner that QSBS tax incentives jumpstart the US national economy and generate strategic job creation, similar tax relief incentives are available to investors in the United Kingdom (UK).
Are tax incentives having the intended effect of spurring innovation and driving investors to invest? Exploring the US incentive structure to similar tax incentives in the UK may reveal some insights.
QSBS in the US
QSBS (Qualified Small Business Stock), IRC Section 1202, was enacted in August of 1993 as bipartisan legislation to aid in jolting the US economy out of recession. Senator Dale Bumpers, a key proponent in drafting the legislation almost three decades ago, summed up the advantages of QSBS like this:
“This is a modest tax incentive that holds great promise for hundreds of thousands of small firms with good ideas but not enough capital.”
QSBS tax exemption benefits aim to fuel job growth on a national level by incentivizing founders to start businesses, employees to join them, and investors to fund them.
Becoming a Qualified Small Business, however requires certain criteria to be met (i.e. C-corporation, located in the US, gross assets under $50 million, etc.). Not all such companies qualify however, as QSBS eligibility excludes companies where employees operate as the “product,” such as healthcare workers, accountants, or lawyers to name the few found under Section 1202(e)(3). QSBS requirements must also be met at the security and individual taxpayer level for a taxpayer to qualify for the benefits. Some of these requirements are at the issuance of the stock, and others are during the duration of the shareholder’s holding period.
EIS and SEIS in the UK
EIS (Enterprise Investment Scheme) and SEIS (Seed Enterprise Investment Scheme) are similar UK government tax relief initiatives incorporated by the British government to incentivize private equity investing in strategically innovative high-risk startup companies by offering investors profitable tax breaks.
EIS was introduced in the UK in 1994 to aid in small business growth and development by generating an influx of capital from investors who were incentivized to invest in this risky market through lucrative tax breaks.
Generally, EIS focuses on mid-sized early-stage companies. EIS allows investors to invest up to £1 million (approx. $1.3 million) a year and get a 30% tax deduction. Capital gains tax rates in the UK vary from 10-28% depending on whether an investor is a basic rate taxpayer or a higher rate taxpayer, determined by income levels. The basic rate, between £12,571 to £50,270 (approx. $16,433 to $65,713) is taxed at a rate of 20%, whereas the higher rate of 40% is for income levels between £50,271 to £150,000 (approx. $65,714 to $196,079). After 3 years, investors do not have to pay capital gains tax on any profits resulting from the sale of shares. If the shares are sold at a loss, investors can also deduct the loss from their capital gains tax.
SEIS began in the UK in 2012 to incentivize investments in companies at their earliest “startup” stage by offering a significant tax break to back risky investment opportunities.
SEIS focuses on the earliest stage startup companies. With SEIS, investors can invest up to £100,000 (approx $130,000) in a given tax year and get a 50% tax break. Capital gains from the sale of shares can result in an exemption from capital gains tax after three years. In addition, if these shares are sold at a loss, investors can deduct their capital gain tax on the sale.
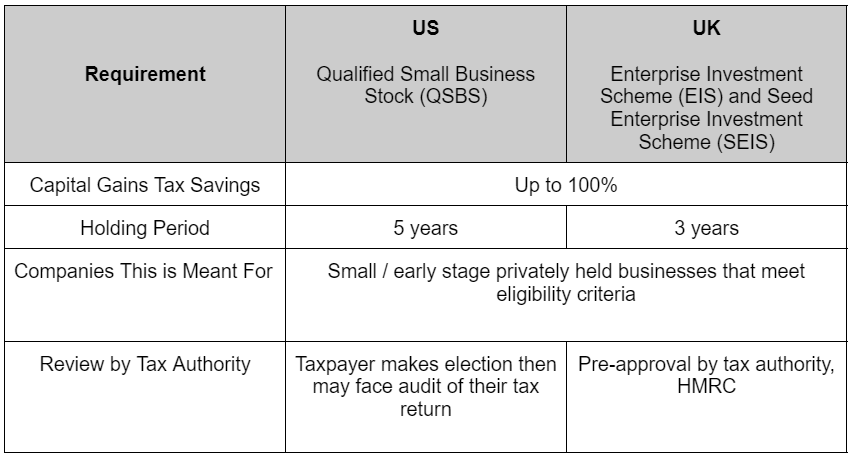
Key Similarities and Differences Between the UK and US Tax Incentives
These various tax incentives (SEIS, EIS, and QSBS) operate to encourage investment in innovative small business sectors that contribute to job creation and national economic growth. However, one major difference between the UK and US tax incentives is in how the tax incentives are approved:
- US tax generally relies on the “honor system” approach, and this is the same for QSBS. A taxpayer files the exclusion on their tax return and the IRS then reviews it.
- UK tax reliefs, SEIS/EIS, require government approval prior to the shareholder claiming the benefit.
Further delineating the key similarities and differences between QSBS in the US and SEIS/EIS in the UK, we note:
Does Knowing about Tax Incentive Eligibility Drive Investor Behavior?
These tax incentives line up well with the early stages of many companies who raise funds on popular and growing crowdfunding platforms. Comparing listings on US versus UK crowdfunding platforms, however it becomes apparent that visibility is a key difference that could impact investor behavior. On UK Crowdfunding platforms, like SEEDRS and Crowdcube, there are tags on the campaign pages indicating if specific investments are SEIS or EIS eligible. This tagging allows for more transparent and convenient visibility of tax relief status for potential investors.
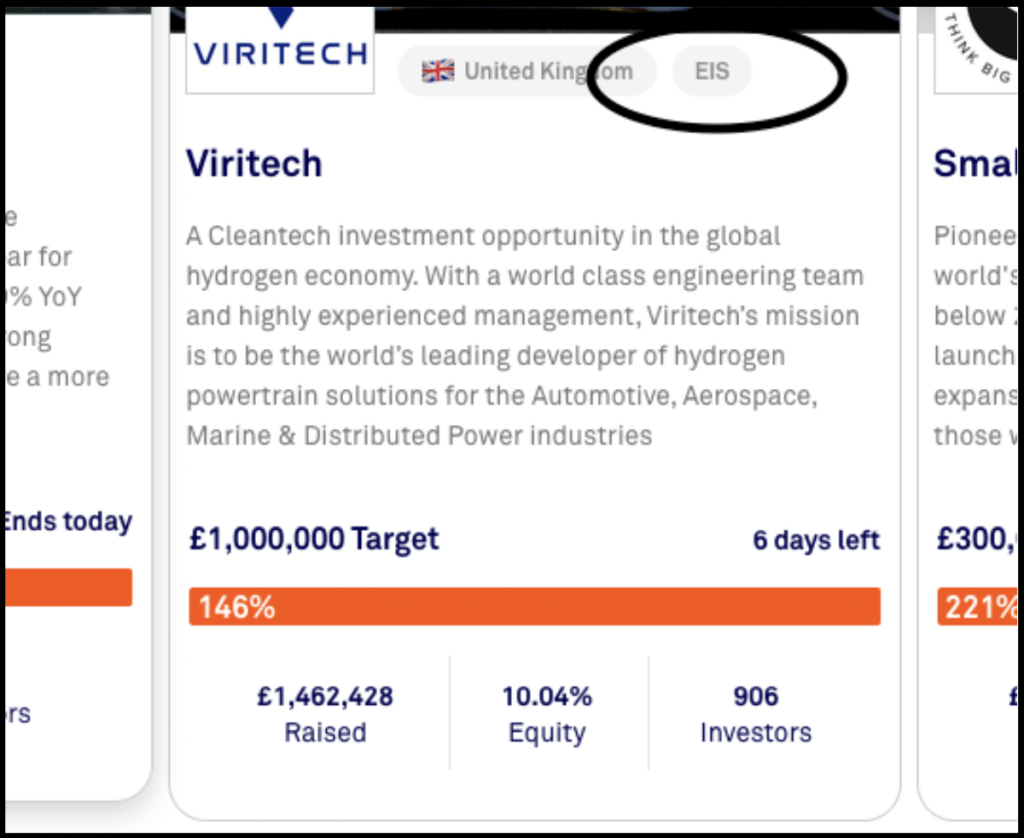
We are not aware of any US crowdfunding platforms indicating if an investment may be QSBS eligible. Certainly the nature of the incentives being pre-approved in the UK makes it more apparent to provide those details to investors in the UK, however just because the IRS doesn’t pre-approve securities as QSBS eligible doesn’t mean that these lucrative tax incentives should be ignored – after all, the incentives were specifically designed to drive investment into the types of companies promoting themselves through crowdfunding.
As President Obama said during the 2012 JOBS act signing,
“start-ups and small business will now have access to a big, new pool of potential investors — namely, the American people. For the first time, ordinary Americans will be able to go online and invest in entrepreneurs that they believe in.”
Would making QSBS more known to the American crowdfunders drive further investment? The difference in tax incentive visibility on UK versus US crowdfunding platforms raises questions surrounding whether or not this tax incentive tagging process leads to more investments.
According to a report released by Statista in June of 2021, the annual market value of equity crowdfunding in the UK, in 2020, was just shy of 550 million British pounds (approximately $726 million). A report by KingsCrowd released in 2021, showed approximately $211 million raised, in 2020, on crowdfunding platforms for the US, nearly a quarter of the total amount invested in the UK.
This stark difference in US and UK equity crowdfunding in 2020 could be related to numerous contributing factors; however, it does beg the question: could the tagging of tax benefits incentivize more equity investments? The greater visibility of tax breaks available to investors may play a part in swinging the pendulum toward increased investor confidence, further encouraging investments that fuel the startup marketplace.
Here at Capgains.com, we aim to make the highly-detailed and nuanced components of the QSBS easier for investors to navigate so they can claim the tax provision with confidence.
Our team of QSBS experts specializes in making the process of determining QSBS eligibility as successful and streamlined as possible for corporations and investors by ensuring shares are eligible and by monitoring QSBS stock eligibility over time. Interested in learning more? Please contact us.
This article does not constitute legal or tax advice. Please consult with your legal or tax advisor with respect to your particular circumstance.

